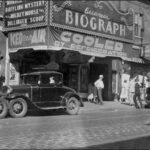A General Process for Making Wine July 1st, 2019 
A General Process for Making Wine.
- Gathering the Fruit
- Picking the Fruit
- Bruising the Fruit
- Vatting the Fruit
- Vinous Fermentation
- Drawing the Must
- Pressing the Must
- Casking the Must
- Spirituous Fermentation
- Racking the Wine
- Bottling and Corking the Wine
- Drinking the Wine
GATHERING THE FRUIT.
It is of considerable consequence to the making of good Wine, that attention be paid to the state and condition of fruit. Fruit of every sort should be gathered in fine weather; those of the berry kind often appear ripe to the eye before they really are so, therefore it is requisite to taste them several times in order to ascertain that they are arrived at the crisis of maturity. This is an important point to the making excellent wine. If fruit be not ripe, the wine will be harsh and hard, unpleasant to the palate, and more so to the stomach; it will also require more spirit and saccharine, and take a longer time to be fit for the table if ever it be spring. if fruit be too ripe, the wine from it will be faint, low and vapid, it will not be strong and generous, it will also require more trouble, additional spirit and expense.
PICKING THE FRUIT.
That is, detaching the unripe and bad berries. The process is certainly a little tedious, but the result when the wine is drunk, of such fruit, will in its richness and quality be most eminently superior. Grapes also should have their stalks picked from them previous to their being placed in the vat.
BRUISING THE FRUIT.
A considerable advantage is gained by this operation in time and bulk. Besides, it prepares the fruit for nature’s hermetical elaboration. The quantity of fruit for making a vintage of domestic wine, is not so large but it may be bruised in a tub, and from thence removed into the vat, or if a very small quantity it may be bruised in the vat. While the fruit is picking by one person, another may bruise it, and as it is bruised remove it into the vat. (When Malaga or Smyrna Raisins are used, they are to be put into the vat with water, to soak, and the following day taken out and bruised, the returned in the vat again, and the general process is to follow.)
VATTING THE FRUIT.
The first thing to be done, is placing a huc-muc or guard, on the inside of the vat against the tap-hole, to prevent the husks escaping at the time the must is drawn off. Immediately as all the fruit is in the vat the portion of water assigned should be added, then the contents stirrred up with the vat-staff and left to macerate until the next day, when the sugar, tartar, & diluted with some of the liquor, is to be put into the vat, and whole again stirred up. The place where the vat is situated should be perfectly free from any working matter, or disagreeable smell; and temperature of not less than 58 degrees.
If a vinous fermentation do not take place, in a reasonable tie, the contents must be often stirred, and the temperature of the place made warmer.
VINOUS FERMENTATION.
This may be said to be a Divine operation which the Omniscient Creator has placed in our cup of life, to transmute the fruits of the Earth, into wine, for the benefit and comfort of his Creatures.
The causes that produce the effects of vinous fermentation are imperfectly known, for no chemical exploration as yet has been able to discover but a few well-ascertained facts.
The time of a vinous fermentation commencing, is always uncertain; it depends much on the quality and quantity of the contents of the vat, to its local situation, to the season or weather, and most particularly to the greenness or ripeness of the fruit.
To produce medium vinous fermentation the vats and contents ought to be placed in a temperature from 50 to 70 degrees. And if this is found not to produce fermentation in a short time, the temperature of the place must be still made warmer and the component matters often stirred with the vat-staff.
The commencement of vinous fermentation may be pretty well known by plunging the thermometer into the middle of the contents of the vat, for a minute, and when taken out, if a fermentation has commenced the temperature of the contents will be higher than the place where the vats are situated.
Shortly after this, the vinous fermentation begins to be very conspicuous and may very easily known by its taste, smell, appearance, and effects.
The contents will first gently rise, and swell with a slight movement and a little hissing.—Some time after, a considerable motion will take place, the contents will also increase in heat, and bulk, and at this crisis a quantity of air escapes. These effects continue a long time changing and decomposing the primordial substances.
It is the elaboration of the vinous fermentation that decomposes the saccharine, produces spirit in wine, and renders it wholesome: hence may be perceived the indispensable necessity of it.
When the vinous fermentation is about half over, the flavoring ingredients are to be put into the vat and well stirred into the contents.
If almonds form a component part, they are first to be beaten to a paste and mixed with a pint or two of the must.—Nutmegs, Cinnamon, Ginger, Seeds, etc. should, before they are put in the vat, be reduced to powder, and mixed with some of the must.
It is impossible to lay down an exact time for a vinous fermentation; but for eighteen gallons, two or three days are generally sufficient for white wines; red wines may have a day or two more.
Towards the end of the vinous fermentation, the agitation, effervescence, and discharges of air cease. The must also in the vat will give, by tasting, a strong vinous pungency to the tongue. This is the period (in order to have strong and generous wine) to stop the remaining slight fermentation by drawing off the must.
DRAWING THE MUST.
Must is the name of the new wine, before it has gone though all the requisite processes and is perfected.
A cock, or spicket and faucet is to be put into the tap-hole of the vat, and the must drawn off immediately and put into open vessels, there to remain until until the pressing is finished.
PRESSING THE HUSK.
As soon as all the must is drawn off from the vat, the husks(residuum) are to be put into hair-bags, the mouth of the bags is to be well fastened, then put into the press and the whole of the vintage pressed without delay.
When the pressing is all finished, the must that is pressed out is to be mixed with the must that was drawn off from the vat.
Many ways may be contrived for pressing a small vintage, for those persons who cannot afford to purchase a proper wine-press. And any hedge-carpenter can contrive a temporary press, with two short flat boards and a long heavy pole to act as a lever. A thing of this sort may be made to have very great power.
Several wines, here treated of, do not require pressing; such wines may be strained through a sweet, clean, canvas bag made with a pointed and downwards sufficiently large to contain the residuum
CASKING THE MUST.
The must may be casked in the place where the vintage is performed, or for conveniency it may taken in portions to the cellar. Each cask is to be filled, within about an inch of the bung-hole, which should be covered over, lightly with a flat bit of wood, or some other light matter that will answer the same purpose. This and the two last processes ought to be performed with alacrity.
The vinous fermentation is now no more and it is very conspicuosly so by the cessation, the must being perfectly cool and calm, and it will remain in this state until a spiritous fermentation. commences.
SPIRITUOUS FERMENTATION.
The spirituous fermentation differs from the vinous; it is essentially necessary to the clarification, the goodness, and perfection of the wine. And it may be said to be the last natural operation in the process of the vintage.
If the vinous fermentation has been well conducted, and the wine cellar be not too cold, a spirituous fermentation will commence in a few days. But this will only be just perceptible by a little hissing, a slight effervescence, and the bit of wood on the bung-hole will move up and down at times in consequence of the discharges of the remaining air (gas.)
This spirituous fermentation will abate in six or twelve days, the time depending on circumstances, on the quality and quantity of the WINE, the liquor being now intitled to this last appellation. The Brandy or spirit assigned should at this time be put to the wine by pouring it in gently without disturbing the wine. No doubt need be entertained but that an association will soon take place between the spirit and the wine as effectually as if it had all been mixed together by agitation. The cask now if not full, just be filled up and bunged hand-tight with (if possible), a wooden bung covered with a piece of new canvas much larger than the bung, in order that the bung may be at any time taken out with more facility. In about a month after the spirit has been added, the cask will again want filling up, this should be done with (if to be had) the overplus of the vintage, if not with some other good wine. The cask must now be bunged up tight.
After this the cask is to be pegged once a month or oftener to see if the wine be clear and not thick, and as soon as it is perceived fine and bright it is to be racked off its lees.
RACKING THE WINE.
If the fermentations have been carried on well, it is of considerable importance to the excellence of all wines, and also to an early racking of them.
This is an operation highly requisite to the keeping wine good; to its purification, strength, color, brillianey, goût, and aroma, and it is performed by drawing off the wine and leaving the lees in the cask. A siphon should be used for this purpose, but if not, the cask must be tapped(with a cock) two or three days previously to the wine being racked off.
It may be racked off into another cask, or into a vat or tub, and returned into the same cask again, after it has been well cleaned; and, if requisite, the cask may be slightly fumigated, immediately before the wine is returned into it. The wine is now to be tasted, and if found to be very weak, a little spirit is to be given to it, the cask filled up and bunged tight.
The process of racking ought to be performed in the temperate weather, and as soon after settles? as the wines appear any way clear, for perhaps a second racking may make them perfectly brilliant, and if so they will want no setting? this is highly advantageous to any wines, but most particular to red wines.
FINING THE WINE.
Many wines improperly made, or made of bad fruit, require fining before they are racked, nevertheless the operation of fining is not always necessary. Most wines well made, do not want fining; this point must first be ascertained, by drawing off a little of the wine into a glass from the peg-hole, in front of the cask and if it be found not perfectly brilliant, it is then to be fined.
Many are the means and materials for fining distempered wines, but for those lately made, and in health, the following methods will give them exquisite limpidity.
One pound of fresh Marsh-Mallow Roots, washed clean, and cut into small pieces; macerate them in two quarts of soft water, twenty four hours, the gently boil the liquor down to three half pints, strain it, and when cold mix with it half an once of pipe-clay or chalk, in powder, then pour the mucilage into the cask, stir up the wine so as not to disturb the lees and leave the vent-peg out for some days after.
Or boiled rice, two table spoonfuls, the whit of one new egg, and half an ounce of burnt allum, in powder. Mix those matters up with a pint or more of the wine, then pour the mucilage into the cask and stir up the wine with a stout stick, but so as not to agitate the lees.
Or, dissolve, in a gentle heat, half an ounce of isinglass in a pint or more of the wine, then mix with it half an once of chalk, in powder; when the two are well incorporated, pour it into the cask and stir up the wine, but so as not to disturb the lees.
As soon as wines are clear and bright, after being fined down, they ought to be racked into a sweet, clean, cask, the cask filled up and bunged tight.
BOTTLING AND CORKING.
Fine clear weather is best for bottling all sorts of wines, and much cleanliness is required in this operation. The first consideration, in bottling wines, is to examine and see if the wines are in a proper state for this purpose. It is folly to attempt bottling, before the wines are fine and brilliant, as they will never brighten after.
Before this operation is commenced all the apparatus is to be in readiness.—The bottles must be all sound, clean, and dry, with plenty of good sound corks, as much depends on them; surely no one would wittingly spoil a bottle of good wine for the sake of using a bad cork.
A finger ought to introduced into the neck of each bottle, as they are corked; by this means it is ascertained what cork will best fit each of them. The small end of the cork that enters the bottle, is first to be squeezed with, if convenient, blunt iron or wooden pincers.
The cork is to be put in with the hand, and then driven well in with the flat wooden mallet, the weight of which ought to be a pound and a quarter, but however not to exceed a pound and half, for if the mallet be too light or too heavy, it will not drive the cork properly, and is also liable to break the bottle. The corks must so completely fill up the neck of each bottle as to render them air tight, if they are not, the cork must be withdrawn and another put in. The corker must so manage as to leave a space of an inch between the wine and the cork.
When all the wine is bottled, it is to be stored in a cool cellar, and on no account on the bottles’ bottoms, but on their sides, and saw-dust, if to be had, if not moss or hay, put copiously between them to prevent their breaking, which would of course waste the wine.
DRINKING.
The moderns are pretty well acquainted with the delights of the bottle, or in other words with the enchanting effects of good wine, nevertherless a few remarks may be made.
Wines, whatever their color may be, ought, when drunk, to be clear and brilliant, for the same wines if not so, will not be so wholesome, nor will they have their proper fine goût.
Wines that have not age given them will not drink, by manly degrees, so potent as they would have done had that been granted.
Wines are known by their taste, brightness, color, aroma.—The requisite criterion of truly good wines are, that they possess strength, beauty, fragrance, coolness, and briskness.
Family made wines seldom have fair play, they are mostly drunk nearly as soon as made. How can individuals expect their wines to be good, generous, and drink well under such improper circumstances.
For the sake of information, on this subject, and shew that wines well made, of the fruits of this country will keep may years and improve thereby, I will just say a word relative to the wine I made in 1803.
To produce a wine approximating those of Madeira, or the best white wine of Minorca was my intention, and the success was equal to my expectations.
The wine was made almost neat of the fruit, only six gallons of water, twenty five pounds of saccharine, and one gallon of brandy, was employed in the product of one hundred and thirty seven gallons of wine.
As all the operations had been well performed, I determined preserving a sample of the wine, in order to ascertain how long an English-made wine, of fruits of our own country, might be kept good and generous.—The wine has been tasted this day, Easter Monday, 1814, and it is found to be strong, brilliant fragrant, and sufficiently Frisca.
From A Treatise on Family Wine Making by P.P. Carnell, ESQ. F.H.S. etc, etc. 1814
Home
Top of Pg.
|
The arsenicals (compounds which contain the heavy metal element arsenic, As) have a long history of use in man – with both benevolent and malevolent intent. The name ‘arsenic’ is derived from the Greek word ‘arsenikon’ which means ‘potent'”. As early as 2000 BC, arsenic trioxide, obtained from smelting copper, was used [...] Read more →
Looking to spice up your dinner? Let’s hop along and cook some roo. Home Top of Pg. Read more →
July 9, 1898. Forest and Stream Pg. 25 Some Notes on American Ship-Worms. [Read before the American Fishes Congress at Tampa.] While we wish to preserve and protect most of the products of our waters, these creatures we would gladly obliterate from the realm of living things. For [...] Read more →
From The How and When, An Authoritative reference reference guide to the origin, use and classification of the world’s choicest vintages and spirits by Hyman Gale and Gerald F. Marco. The Marco name is of a Chicago family that were involved in all aspects of the liquor business and ran Marco’s Bar [...] Read more →
IT requires a far search to gather up examples of furniture really representative in this kind, and thus to gain a point of view for a prospect into the more ideal where furniture no longer is bought to look expensively useless in a boudoir, but serves everyday and commonplace need, such as [...] Read more →
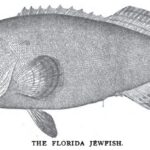
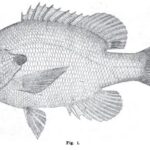
Nov. 5. 1898 Forest and Stream Pg. 371-372 The Black Grouper or Jewfish. New Smyrna, Fla., Oct. 21.—Editor Forest and Stream: It is not generally known that the fish commonly called jewfish. warsaw and black grouper are frequently caught at the New Smyrna bridge [...] Read more →
Snipe shooting-Epistle on snipe shooting, from Ned Copper Cap, Esq., to George Trigger-George Trigger’s reply to Ned Copper Cap-Black partridge. —— “Si sine amore jocisque Nil est jucundum, vivas in &more jooisque.” -Horace. “If nothing appears to you delightful without love and sports, then live in sporta and [...] Read more →
Eadweard Muybridge was a fascinating character. Click here to learn how Eadweard committed “Justifiable Homicide” after shooting his wife’s lover in 1874. Home Top of Pg. Read more →
Reprint from The Royal Collection Trust website: Kneller was born in Lubeck, studied with Rembrandt in Amsterdam and by 1676 was working in England as a fashionable portrait painter. He painted seven British monarchs (Charles II, James II, William III, Mary II, Anne, George I and George II), though his [...] Read more →
“The Leda, in the Colonna palace, by Correggio, is dead-coloured white and black, with ultramarine in the shadow ; and over that is scumbled, thinly and smooth, a warmer tint,—I believe caput mortuum. The lights are mellow ; the shadows blueish, but mellow. The picture is painted on panel, in [...] Read more →
From Dr. Marvel’s 1929 book entitled Hoodoo for the Common Man, we find his infamous Hoochie Coochie Hex. What follows is a verbatim transcription of the text: The Hoochie Coochie Hex should not be used in conjunction with any other Hexes. This can lead to [...] Read more →
Take to every quart of water one pound of Malaga raisins, rub and cut the raisins small, and put them to the water, and let them stand ten days, stirring once or twice a day. You may boil the water an hour before you put it to the raisins, and let it [...] Read more →
Aw, the good old days, meet in the coffee shop with a few friends, click open the Zippo, inhale a glorious nosegay of lighter fluid, fresh roasted coffee and a Marlboro cigarette…. A Meta-analysis of Coffee Drinking, Cigarette Smoking, and the Risk of Parkinson’s Disease We conducted a [...] Read more →
Home Top of Pg. Read more →
Officers and men of the 13th Light Dragoons, British Army, Crimea. Rostrum photograph of photographer’s original print, uncropped and without color correction. Survivors of the Charge. Half a league, half a league, Half a league onward, All in the valley of Death Rode the six hundred. “Forward, the Light Brigade! Charge for the [...] Read more →
? This video by AT Restoration is the best hands on video I have run across on the basics of classic upholstery. Watch a master at work. Simply amazing. Tools: Round needles: https://amzn.to/2S9IhrP Double pointed hand needle: https://amzn.to/3bDmWPp Hand tools: https://amzn.to/2Rytirc Staple gun (for beginner): https://amzn.to/2JZs3x1 Compressor [...] Read more →
EIGHTEEN GALLONS is here give as a STANDARD for all the following Recipes, it being the most convenient size cask to Families. See A General Process for Making Wine If, however, only half the quantity of Wine is to be made, it is but to divide the portions of [...] Read more →
H.F. Leonard was an instructor in wrestling at the New York Athletic Club. Katsukum Higashi was an instructor in Jujitsu. “I say with emphasis and without qualification that I have been unable to find anything in jujitsu which is not known to Western wrestling. So far as I can see, [...] Read more →
PEACH BRANDY 2 gallons + 3 quarts boiled water 3 qts. peaches, extremely ripe 3 lemons, cut into sections 2 sm. pkgs. yeast 10 lbs. sugar 4 lbs. dark raisins Place peaches, lemons and sugar in crock. Dissolve yeast in water (must NOT be to hot). Stir thoroughly. Stir daily for 7 days. Keep [...] Read more →
The Queen Elizabeth Trust, or QEST, is an organisation dedicated to the promotion of British craftsmanship through the funding of scholarships and educational endeavours to include apprenticeships, trade schools, and traditional university classwork. The work of QEST is instrumental in keeping alive age old arts and crafts such as masonry, glassblowing, shoemaking, [...] Read more →
THE ABC OF THE FEDERAL RESERVE SYSTEM WH Y THE FEDERAL RESERVE SYSTEM WAS CALLED INTO BEING, THE MAIN FEATURES OF ITS ORGANIZATION , AND HOW IT WORKS B Y EDWIN WALTER KEMMERER, PH.D. PROFESSOR OF ECONOMICS AND FINANCE IN PRINCETON UNIVERSITY AND MEMBER OF [...] Read more →
Full Cover, rear, spine, and front Published by Piranesi Press in collaboration with Country House Essays, this beautiful paperback version of the King James Bible is now available for $79.95 at Barnes and Noble.com This is a limited Edition of 500 copies Worldwide. Click here to view other classic books [...] Read more →
Twinings London – photo by Elisa.rolle Is the tea in your cup genuine? The fact is, had one been living in the early 19th Century, one might occasionally encounter a counterfeit cup of tea. Food adulterations to include added poisonings and suspect substitutions were a common problem in Europe at [...] Read more →
Como dome facade – Pliny the Elder – Photo by Wolfgang Sauber Work in Progress… THE VARNISHES. Every substance may be considered as a varnish, which, when applied to the surface of a solid body, gives it a permanent lustre. Drying oil, thickened by exposure to the sun’s heat or [...] Read more →
Home Top of Pg. Read more →
Mortlake Tapestries at Chatsworth House Click here to learn more about the Mortlake Tapestries of Chatsworth The Mortlake Tapestries were founded by Sir Francis Crane. From the Dictionary of National Biography, 1885-1900, Volume 13 Crane, Francis by William Prideaux Courtney CRANE, Sir FRANCIS (d. [...] Read more →
Home Top of Pg. Read more →
To learn more about Julian McDonnell, film director, click here. Home Top of Pg. Read more →
Home Top of Pg. Read more →
. Home Top of [...] Read more →
Are you considering purchasing a copper water pitcher for storing drinking water but have questions about the effects on your health? The following study may help jump-start your research. Storing Drinking-water in Copper pots Kills Contaminating Diarrhoeagenic Bacteria ABSTRACT Microbially-unsafe water is [...] Read more →
Salmon and Sturgeon Caviar – Photo by Thor Salmon caviar was originated about 1910 by a fisherman in the Maritime Provinces of Siberia, and the preparation is a modification of the sturgeon caviar method (Cobb 1919). Salomon caviar has found a good market in the U.S.S.R. and other European countries where it [...] Read more →
Banana Propagation Reprinted from the International Institute of Tropical Agriculture (IITA.org) The traditional means of obtaining banana planting material (“seed”) is to acquire suckers from one’s own banana garden, from a neighbor, or from a more distant source. This method served to spread common varieties around the world and to multiply them [...] Read more →
Click here to read the full text of the Hunting Act – 2004 Home Top of Pg. Read more →
Home Top of Pg. Read more →
Home Top of Pg. Read more →
German made shotguns by Krieghoff, founded in 1886. Home Top of Pg. Read more →
Chipping a Turpentine Tree DISTILLING TURPENTINE One of the Most Important Industries of the State of Georgia Injuring the Magnificent Trees Spirits, Resin, Tar, Pitch, and Crude Turpentine all from the Long Leaved Pine – “Naval Stores” So Called. Dublin, Ga., May 8. – One of the most important industries [...] Read more →
Muscadine Jelly 6 cups muscadine grape juice 6 cups sugar 1 box Kraft Sure Gel or Ball Fruit Jell Home Top of [...] Read more →
A terrestial globe on which the tracts and discoveries are laid down from the accurate observations made by Capts Cook, Furneux, Phipps, published 1782 / globe by John Newton ; cartography by William Palmer, held by the State Library of New South Wales The British Library, using sophisticated filming equipment and software, [...] Read more →
Biograph Theater, where John Dillinger was gunned down by the FBI on July 22, 1934 The Great Depression was on—highway based crime was rampant, the gangsters dressed as well as the bankers they robbed, and and Henry Ford’s big beautiful V8 sedan was the getaway car of choice for both wheelman and [...] Read more →
Over the years I have observed a decline in manners amongst young men as a general principle and though there is not one particular thing that may be asserted as the causal reason for this, one might speculate… Self-awareness and being aware of one’s surroundings in social interactions [...] Read more →
There is nothing more delightful than a great poetry reading to warm ones heart on a cold winter night fireside. Today is one of the coldest Valentine’s days on record, thus, nothing could be better than listening to the resonant voice of Robin Shuckbrugh, The Cotswold [...] Read more →
Click here to visit Ovation Guitars Ovation Patent Drawing 1975 Click here to read a copy of the 1975 Patent for the Ovation Guitar Home Top of Pg. Read more →
Sucker The components of any given market place include both physical structures set up to accommodate trading, and participants to include buyers, sellers, brokers, agents, barkers, pushers, auctioneers, agencies, and propaganda outlets, and banking or transaction exchange facilities. Markets are generally set up by sellers as it is in their [...] Read more →
Jujitsu training 1920 in Japanese agricultural school. CHAPTER V THE VALUE OF EVEN TEMPER IN ATHLETICS—SOME OF THE FEATS THAT REQUIRE GOOD NATURE In the writer’s opinion it becomes necessary to make at this point some suggestions relative to a very important part of the training in jiu-jitsu. [...] Read more →
Mortlake Tapestries at Chatsworth House Click here to read copy of Daemonologie Home Top of Pg. Read more →
Vintage woodcut illustration of a Eel This dish is a favorite in Northern Europe, from the British Isles to Sweden. Clean and skin the eels and cut them into pieces about 3/4-inch thick. Wash and drain the pieces, then dredge in fine salt and allow to stand from 30 [...] Read more →
Home Top of Pg. Read more →
Royal Exchange and The Bank of England From How to Make Money; and How to Keep it, Or, Capital and Labor based on the works of Thomas A. Davies Revised & Rewritten with Additions by Henry A. Ford A.M. – 1884 CHAPTER XXVI BANKING AND INSURANCE. I [...] Read more →
Stoke Park Pavillions Stoke Park Pavilions, UK, view from A405 Road. photo by Wikipedia user Cj1340 From Wikipedia: Stoke Park – the original house Stoke park was the first English country house to display a Palladian plan: a central house with balancing pavilions linked by colonnades or [...] Read more →
An angler with a costly pole Surmounted with a silver reel, Carven in quaint poetic scroll- Jointed and tipped with finest steel— With yellow flies, Whose scarlet eyes And jasper wings are fair to see, Hies to the stream Whose bubbles beam Down murmuring eddies wild and free. And casts the line with sportsman’s [...] Read more →
Mudlarks of London Mudlarking along the Thames River foreshore is controlled by the Port of London Authority. According to the Port of London website, two type of permits are issued for those wishing to conduct metal detecting, digging, or searching activities. Standard – allows digging to a depth of 7.5 [...] Read more →
Foie gras with Sauternes, Photo by Laurent Espitallier As an Appetizer Pale dry Sherry, with or without bitters, chilled or not. Plain or mixed Vermouth, with or without bitters. A dry cocktail. With Oysters, Clams or Caviar A dry flinty wine such as Chablis, Moselle, Champagne. Home Top of [...] Read more →
Home Top of Pg. Read more →
Home Top of Pg. Read more →
Reprint from The Pitfalls of Speculation by Thomas Gibson 1906 Ed. THE PUBLIC ATTITUDE TOWARD SPECULATION THE public attitude toward speculation is generally hostile. Even those who venture frequently are prone to speak discouragingly of speculative possibilities, and to point warningly to the fact that an [...] Read more →
Sept. 3, 1898. Forest and Stream Pg. 188-189 How to Distinguish Fishes. BY FRED MATHER. The average angler knows by sight all the fish which he captures, but ask him to describe one and he is puzzled, and will get off on the color of the fish, which is [...] Read more →
How happy is he born and taught. That serveth not another’s will; Whose armour is his honest thought, And simple truth his utmost skill Whose passions not his masters are; Whose soul is still prepared for death, Untied unto the world by care Of public fame or private breath; Who envies none that chance [...] Read more →
Noel Desenfans and Sir Francis Bourgeois, circa 1805 by Paul Sandby, watercolour on paper The Dulwich Picture Gallery was England’s first purpose-built art gallery and considered by some to be England’s first national gallery. Founded by the bequest of Sir Peter Francis Bourgois, dandy, the gallery was built to display his vast [...] Read more →
It was a strange assignment. I picked up the telegram from desk and read it a third time. NEW YORK, N.Y., MAY 9, 1949 HAVE BEEN INVESTIGATING FLYING SAUCER MYSTERY. FIRST TIP HINTED GIGANTIC HOAX TO COVER UP OFFICIAL SECRET. BELIEVE IT MAY HAVE BEEN PLANTED TO HIDE [...] Read more →
ORIGIN OF THE APOTHECARY. The origin of the apothecary in England dates much further back than one would suppose from what your correspondent, “A Barrister-at-Law,” says about it. It is true he speaks only of apothecaries as a distinct branch of the medical profession, but long before Henry VIII’s time [...] Read more →
NAPOLEON’S PHARMACISTS. Of the making of books about Napoleon there is no end, and the centenary of his death (May 5) is not likely to pass without adding to the number, but a volume on Napoleon”s pharmacists still awaits treatment by the student in this field of historical research. There [...] Read more →
CENTRAL INTELLIGENCE AGENCY INROMATION FROM FOREIGN DOCUMENT OR RADIO BROADCASTS COUNTRY: Non-Orbit SUBJECT: Military – Air – Scientific – Aeronautics HOW PUBLISHED: Newspapers WHERE PUBLISHED: As indicated DATE PUBLISHED: 12 Dec 1953 – 12 Jan 1954 LANGUAGE: Various SOURCE: As indicated REPORT NO. 00-W-30357 DATE OF INFORMATION: 1953-1954 DATE DIST. 27 [...] Read more →
King Leopold Butcher of the Congo For the somewhat startling suggestion in the heading of this interview, the missionary interviewed is in no way responsible. The credit of it, or, if you like, the discredit, belongs entirely to the editor of the Review, who, without dogmatism, wishes to pose the question as [...] Read more →
Add 3 quarts clover blossoms* to 4 quarts of boiling water removed from heat at point of boil. Let stand for three days. At the end of the third day, drain the juice into another container leaving the blossoms. Add three quarts of fresh water and the peel of one lemon to the blossoms [...] Read more →
Liquorice, the roots of Glycirrhiza Glabra, a perennial plant, a native of the south of Europe, but cultivated to some extent in England, particularly at Mitcham, in Surrey. Its root, which is its only valuable part, is long, fibrous, of a yellow colour, and when fresh, very juicy. [...] Read more →
Reprint from The Pitfalls of Speculation by Thomas Gibson 1906 Ed. THE PUBLIC ATTITUDE TOWARD SPECULATION THE public attitude toward speculation is generally hostile. Even those who venture frequently are prone to speak discouragingly of speculative possibilities, and to point warningly to the fact that an overwhelming majority [...] Read more →
A General Process for Making Wine. Gathering the Fruit Picking the Fruit Bruising the Fruit Vatting the Fruit Vinous Fermentation Drawing the Must Pressing the Must Casking the Must Spirituous Fermentation Racking the Wine Bottling and Corking the Wine Drinking the Wine GATHERING THE FRUIT. It is of considerable consequence [...] Read more →
BOOKS CONDEMNED TO BE BURNT. By JAMES ANSON FARRER, LONDON ELLIOT STOCK, 62, PATERNOSTER ROW 1892 ———- WHEN did books first come to be burnt in England by the common hangman, and what was [...] Read more →
Paul Thorpe, Brighton, U.K. The YouTube watch collecting world is rather tight-knit and small, but growing, as watches became a highly coveted commodity during the recent world-wide pandemic and fueled an explosion of online watch channels. There is one name many know, The Time Piece Gentleman. This name for me [...] Read more →
First Pineapple Grown in England Click here to read an excellent article on the history of pineapple growing in the UK. Should one be interested in serious mass scale production, click here for scientific resources. Growing pineapples in the UK. The video below demonstrates how to grow pineapples in Florida. [...] Read more →
A Real Soda Jerk FORMULAS FROM VARIOUS SOURCES. Pineapple Frappe. Water, 1 gallon; sugar 2 pounds of water. 61/2 pints, and simple syrup. 2 1/2 pints; 2 pints of pineapple stock or 1 pint of pineapple stock and 1 pint of grated pineapple juice of 6 lemons. Mix, [...] Read more →
Any prudent investor would jump at the chance to receive a guaranteed 6% dividend for life. So how does one get in on this action? The fact of the matter is…YOU can’t…That is unless you are a shareholder of one of the twelve Federal Reserve Banks and the banks under [...] Read more →
Home Top of Pg. Read more →
Home Top of Pg. Read more →
Crewe Hall Dining Room THE transient tenure that most of us have in our dwellings, and the absorbing nature of the struggle that most of us have to make to win the necessary provisions of life, prevent our encouraging the manufacture of well-wrought furniture. We mean to outgrow [...] Read more →
Home Top of Pg. Read more →
Dr. David Starkey, the UK’s premiere historian, speaks to the modern and fleeting notion of “cancel culture”. Starkey’s brilliance is unparalleled and it has become quite obvious to the world’s remaining Western scholars willing to stand on intellectual integrity that a few so-called “Woke Intellectuals” most certainly cannot undermine [...] Read more →
Home Top of Pg. Read more →
Video courtesy of Imperial War Museums, UK Home Top of Pg. Read more →
Click here to read The First Greek Book by John Williams White The First Greek Book - 15.7MB IN MEMORIAM JOHN WILLIAMS WHITE The death, on May 9, of John Williams White, professor of Greek in Harvard University, touches a large number of classical [...] Read more →
Half a league, half a league, Half a league onward, All in the valley of Death Rode the six hundred. “Forward, the Light Brigade! Charge for the guns!” he said. Into the valley of Death Rode the six hundred. Home Top of [...] Read more →
Life insurance certificate issued by the Yorkshire Fire & Life Insurance Company to Samuel Holt, Liverpool, England, 1851. On display at the British Museum in London. Donated by the ifs School of Finance. Photo by Osama Shukir Muhammed Amin FRCP(Glasg) From How to Make Money; and How to Keep it, Or, Capital and Labor [...] Read more →
Vishnu as the Cosmic Man (Vishvarupa) Opaque watercolour on paper – Jaipur, Rajasthan c. 1800-50 CLAIRVOYANCE AND OCCULT POWERS By Swami Panchadasi Copyright, 1916 By Advanced Thought Pub. Co. Chicago, Il INTRODUCTION. In preparing this series of lessons for students of [...] Read more →
PAINTER-WORK, in the building trade. When work is painted one or both of two distinct ends is achieved, namely the preservation and the coloration of the material painted. The compounds used for painting—taking the word as meaning a thin protective or decorative coat—are very numerous, including oil-paint of many kinds, distemper, whitewash, [...] Read more →
Donate to the YouTube site owner Gabe and he might send you some chocolate…. Home Top of Pg. Read more →
Blackbeard’s Jolly Roger If you’re looking for that most refreshing of summertime beverages for sipping out on the back patio or perhaps as a last drink before walking the plank, let me recommend my Blunderbuss Mai Tai. I picked up the basics to this recipe over thirty years ago when holed up [...] Read more →
Home Top of Pg. Read more →
Tom Oates, aka Nabokov at en.wikipedia No two commercial tuna salads are prepared by exactly the same formula, but they do not show the wide variety characteristic of herring salad. The recipe given here is typical. It is offered, however, only as a guide. The same recipe with minor variations to suit [...] Read more →
Robert W. Service (b.1874, d.1958) There are strange things done in the midnight sun By the men who moil for gold; The Arctic trails have their secret tales That would make your blood run cold; The Northern Lights have seen queer sights, But the queerest they ever did see Was that night [...] Read more →
Toxicity of Rhododendron From Countrysideinfo.co.UK “Potentially toxic chemicals, particularly ‘free’ phenols, and diterpenes, occur in significant quantities in the tissues of plants of Rhododendron species. Diterpenes, known as grayanotoxins, occur in the leaves, flowers and nectar of Rhododendrons. These differ from species to species. Not all species produce them, although Rhododendron ponticum [...] Read more →
Hunters at Work This is a recipe I created from scratch by trial and error. (Note: This recipe contains no eggs, refined white flour or white sugar.) 2 Cups Whole Wheat Flour – As unprocessed as you can find it 3 Cups of Raw Oatmeal 1 Cup of [...] Read more →
Cleremont Club 44 Berkeley Square, London Home Top of Pg. Read more →
The Racing Knockabout Gosling. Gosling was the winning yacht of 1897 in one of the best racing classes now existing in this country, the Roston knockabout class. The origin of this class dates back about six years, when Carl, a small keel cutter, was built for C. H. [...] Read more →
Chen Lin, Water fowl, in Cahill, James. Ge jiang shan se (Hills Beyond a River: Chinese Painting of the Yuan Dynasty, 1279-1368, Taiwan edition). Taipei: Shitou chubanshe fen youxian gongsi, 1994. pl. 4:13, p. 180. Collection of the National Palace Museum, Taipei. scroll, light colors on paper, 35.7 x 47.5 cm Read more →
July 2, 1898 Forest and Stream, Fresh-Water Angling. No. IX.—The Two Crappies. BY FRED MATHER. Fishing In Tree Tops. Here a short rod, say 8ft., is long enough, and the line should not be much longer than the rod. A reel is not [...] Read more →
INTRODUCTION The idea of compiling this little volume occurred to me while on a visit to some friends at their summer home in a quaint New England village. The little town had once been a thriving seaport, but now consisted of hardly more than a dozen old-fashioned Colonial houses facing [...] Read more →
Home Top of Pg. Read more →
Citrus Fruit Culture THE PRINCIPAL fruit and nut trees grown commercially in the United States (except figs, tung, and filberts) are grown as varieties or clonal lines propagated on rootstocks. Almost all the rootstocks are grown from seed. The resulting seedlings then are either budded or grafted with propagating wood [...] Read more →
by Alan Greenspan, 1967 An almost hysterical antagonism toward the gold standard is one issue which unites statists of all persuasions. They seem to sense-perhaps more clearly and subtly than many consistent defenders of laissez-faire — that gold and economic freedom are inseparable, that the gold standard is an instrument [...] Read more →
THE FOWLING PIECE, from the Shooter’s Guide by B. Thomas – 1811. I AM perfectly aware that a large volume might be written on this subject; but, as my intention is to give only such information and instruction as is necessary for the sportsman, I shall forbear introducing any extraneous [...] Read more →
Hebborn Piranesi Before meeting with an untimely death at the hand of an unknown assassin in Rome on January 11th, 1996, master forger Eric Hebborn put down on paper a wealth of knowledge about the art of forgery. In a book published posthumously in 1997, titled The Art Forger’s Handbook, Hebborn suggests [...] Read more →
Guarea guidonia Recipe 5 Per Cent Alcohol 8-24 Grain – Heroin Hydrochloride 120 Minims – Tincture Euphorbia Pilulifera 120 Minims – Syrup Wild Lettuce 40 Minims – Tincture Cocillana 24 Minims – Syrup Squill Compound 8 Gram – Ca(s)ecarin (P, D, & Co.) 8-100 Grain Menthol Dose – One-half to one fluidrams (2 to [...] Read more →
To Choose Poultry. When fresh, the eyes should be clear and not sunken, the feet limp and pliable, stiff dry feet being a sure indication that the bird has not been recently killed; the flesh should be firm and thick and if the bird is plucked there should be no [...] Read more →
Home Top of Pg. Read more →
*note – Billesdon and Billesden have both been used to name the hunt. BILLESDEN COPLOW POEM [From “Reminiscences of the late Thomas Assheton Smith, Esq”] The run celebrated in the following verses took place on the 24th of February, 1800, when Mr. Meynell hunted Leicestershire, and has since been [...] Read more →
Home Top of Pg. Read more →
DECORATED or “sumptuous” furniture is not merely furniture that is expensive to buy, but that which has been elaborated with much thought, knowledge, and skill. Such furniture cannot be cheap, certainly, but the real cost of it is sometimes borne by the artist who produces rather than by the man who may [...] Read more →
The magician delighted in exposing spiritualists as con men and frauds. By EDMUND WILSON June 24, 1925 Houdini is a short strong stocky man with small feet and a very large head. Seen from the stage, his figure, with its short legs and its pugilist’s proportions, is less impressive than at close [...] Read more →
To Clean Watch Chains. Gold or silver watch chains can be cleaned with a very excellent result, no matter whether they may be matt or polished, by laying them for a few seconds in pure aqua ammonia; they are then rinsed in alcohol, and finally. shaken in clean sawdust, free from sand. [...] Read more →
Home Top of Pg. Read more →
Buying a book for a serious collector with refined tastes can be a daunting task. However, there is one company that publishes some of the finest reproduction books in the world, books that most collectors wouldn’t mind having in their collection no matter their general preference or specialty. Read more →
Home Top of Pg. Read more →
This massive volume gives one a real visual sense of what it was like running a highly efficient colonial operation in the early 20rh Century. It will also go a long way to help anyone wishing to understand modern political intrigue in the Middle-East. Click here to read A Survey of Palestine [...] Read more →
TROF. C. F. HOLDFER AND HIS 183LBS. TUNA, WITH BOATMAN JIM GARDNER. July 2, 1898. Forest and Stream Pg. 11 The Tuna Record. Avalon. Santa Catalina Island. Southern California, June 16.—Editor Forest and Stream: Several years ago the writer in articles on the “Game Fishes of the Pacific Slope,” in [...] Read more →
Modern slow cookers come in all sizes and colors with various bells and whistles, including timers and shut off mechanisms. They also come with a serious design flaw, that being the lack of a proper domed lid. The first photo below depict a popular model Crock-Pot® sold far and wide [...] Read more →
A rhetorical question? Genuine concern? In this essay we are examining another form of matter otherwise known as national literary matters, the three most important of which being the Matter of Rome, Matter of France, and the Matter of England. Our focus shall be on the Matter of England or [...] Read more →
And now for the transformation of Gray Gardens Home Top of Pg. Read more →
NEWSPAPER.-Printed sheets published at stated intervals, chiefly for the purpose of conveying intelligence on current events. The Romans wrote out an account of the most memorable occurrences of the day, which were sent to public officials. They were entitled Acta Durna, and read substantially like the local column of a [...] Read more →
Edwin Austin Abbey. King Lear, Act I, Scene I (Cordelia’s Farewell) The Metropolitan Museum of Art. Dates: 1897-1898 Dimensions: Height: 137.8 cm (54.25 in.), Width: 323.2 cm (127.24 in.) Medium: Painting – oil on canvas Home Top of Pg. Read more →
Over the years I have observed a decline in manners amongst young men as a general principle and though there is not one particular thing that may be asserted as the causal reason for this, one might speculate… Self-awareness and being aware of one’s surroundings in social [...] Read more →
Note on Watercolour: F.A. Molony (fl. 1930-1938) was a Major in the Royal Engineers. The National Army Museum hold his work. His work was also shown at an exhibition of officers work at the R.B.A. Galleries (Army Officers’ Art Society) Description from Youtube: June 2015 will see [...] Read more →
Home Top of Pg. Read more →
What is follows is an historical article that appeared in The Hartford Courant in 1916 about the arsenic murders carried out by Mrs. Archer-Gilligan. This story is the basis for the 1944 Hollywood film “Arsenic and Old Lace” starring Cary Grant and Priscilla Lane and directed by Frank Capra. The [...] Read more →
Roger Scruton by Peter Helm This is one of those videos that the so-called intellectual left would rather not be seen by the general public as it makes a laughing stock of the idiots running the artworld, a multi-billion dollar business. https://archive.org/details/why-beauty-matters-roger-scruton or Click here to watch [...] Read more →
Hernando de Soto (c1496-1542) Spanish explorer and his men torturing natives of Florida in his determination to find gold. Hand-coloured engraving. John Judkyn Memorial Collection, Freshford Manor, Bath The print above depicts Spanish explorer Hernando de Soto and his band of conquistadors torturing Florida natives in order to extract information on where [...] Read more →
Dried Norwegian Salt Cod Fried fish cakes are sold rather widely in delicatessens and at prepared food counters of department stores in the Atlantic coastal area. This product has possibilities for other sections of the country. Ingredients: Home Top of [...] Read more →
Jul. 23, 1898 Forest and Stream, Pg. 65 Horn Measurements. Editor Forest and Stream: “Record head.” How shamefully this term is being abused, especially in the past three years; or since the giant moose from Alaska made his appearance in public and placed all former records (so far as [...] Read more →
Dutch artist Herman de Vries – Photo taken by son Vince The two videos below of Herman de Vries at work at the Venice Bienalle 2015 are quite inspiring. So inspiring in fact that I moved into a cave for two weeks and wrote Shakespearean tragedy with charcoal. Filled with great joy [...] Read more →
The following research discussion is from a study funded by the U.S. National Institute of Health entitled: Boschniakia rossica prevents the carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatotoxicity in rat. It may be of interest to heavy drinkers. Home Top of [...] Read more →
Click here to visit the New Yorkshire YouTube channel. Home Top of Pg. Read more →
King George IV was known far and wide as the dandy king, incompetent, ugly, and vulgar. As Prince regent, prior to his assent to the throne, he kept fast company with Beau Brummel, King of Dandies, a man sixteen years his younger. And decadence followed. King George was a gambler, philanderer, and [...] Read more →
Testing the Irish Blue Terrier Breed in 1923. Home Top of Pg. Read more →
From the classic British Movie, The Shooting Party, a 1985 British drama film directed by Alan Bridges based on Isabel Colegate’s 9th novel of the same name published in 1980 we find a scene set in the billiards parlor whereupon the host of the weekend shooting party Sir Randolph Nettleby walks in [...] Read more →
What follows is a chapter from Nathaniel Bagshaw Ward’s 1852 treatise on terrarium gardening. ON THE NATURAL CONDITIONS OF PLANTS. To enter into any lengthened detail on the all-important subject of the Natural Conditions of Plants would occupy far too much space; yet to pass it by without special notice, [...] Read more →
San Felipe Model Reprinted from FineModelShips.com with the kind permission of Dr. Michael Czytko The SAN FELIPE is one of the most favoured ships among the ship model builders. The model is elegant, very beautifully designed, and makes a decorative piece of art to be displayed at home or in the [...] Read more →
The following recipes form the most popular items in a nine-course dinner program: BIRD’S NEST SOUP Soak one pound bird’s nest in cold water overnight. Drain the cold water and cook in boiling water. Drain again. Do this twice. Clean the bird’s nest. Be sure [...] Read more →
WITCHCRAFT, SORCERY, MAGIC AND OTHER PSYCHOLOGICAL PHENOMENA AND THEIR IMPLICATIONS ON MILITARY AND PARAMILITARY OPERATIONS IN THE CONGO This report has been prepared in response to a query posed by ODCS/OPS, Department of the Army, regarding the purported use of witchcraft, sorcery, and magic by insurgent elements in the Republic [...] Read more →
Furniture Polishing Cream. Animal oil soap…………………….1 onuce Solution of potassium hydroxide…. .5 ounces Beeswax……………………………1 pound Oil of turpentine…………………..3 pints Water, enough to make……………..5 pints Dissolve the soap in the lye with the aid of heat; add this solution all at once to the warm solution of the wax in the oil. Beat [...] Read more →
Dominion, Royal St. Lawrence Yacht Club,Winner of Seawanhaka Cup, 1898. The Tail Wags the Dog. The following is a characteristic sample of those broad and liberal views on yachting which are the pride of the Boston Herald. Speaking of the coming races for the Seawanhaka international challenge cup, it says: [...] Read more →
http://www.vermeerscamera.co.uk/home.htm Home Top of Pg. Read more →
Take the large blue figs when pretty ripe, and steep them in white wine, having made some slits in them, that they may swell and gather in the substance of the wine. Then slice some other figs and let them simmer over a fire in water until they are reduced [...] Read more →
William Wyggeston’s chantry house, built around 1511, in Leicester: The building housed two priests, who served at a chantry chapel in the nearby St Mary de Castro church. It was sold as a private dwelling after the dissolution of the chantries. A Privately Built Chapel Chantry, chapel, generally within [...] Read more →
THE SNIPE, from the Shooter’s Guide by B. Thomas – 1811 AFTER having given a particular description of the woodcock, it will only. be necessary to observe, that the plumage and shape of the snipe is much the same ; and indeed its habits and manners sets bear a great [...] Read more →
BLACKBERRY WINE 5 gallons of blackberries 5 pound bag of sugar Fill a pair of empty five gallon buckets half way with hot soapy water and a ¼ cup of vinegar. Wash thoroughly and rinse. Fill one bucket with two and one half gallons of blackberries and crush with [...] Read more →
Early Texas photo of Tarpon catch – Not necessarily the one mentioned below… July 2, 1898. Forest and Stream Pg.10 Texas Tarpon. Tarpon, Texas.—Mr. W. B. Leach, of Palestine, Texas, caught at Aransas Pass Islet, on June 14, the largest tarpon on record here taken with rod and reel. The [...] Read more →
Click here to access the world’s most powerful Import/Export Research Database on the Planet. With this search engine one is able to access U.S. Customs and other government data showing suppliers for any type of company in the United States. Home Top of Pg. Read more →
It is a pity that the traditions and literature in praise of fly fishing have unconsciously hampered instead of expanded this graceful, effective sport. Many a sportsman has been anxious to share its joys, but appalled by the rapture of expression in describing its countless thrills and niceties he has been literally [...] Read more →
Home Top of Pg. Read more →
|
Home Top of Pg. Read more →
Home Top of Pg. Read more →
Home Top of Pg. Read more →
Liquorice, the roots of Glycirrhiza Glabra, a perennial plant, a native of the south of Europe, but cultivated to some extent in England, particularly at Mitcham, in Surrey. Its root, which is its only valuable part, is long, fibrous, of a yellow colour, and when fresh, very juicy. [...] Read more →
Photo by Greg O’Beirne Home Top of Pg. Read more →
If ever it could be said that there is such a thing as miracle healing soil, Ivan Sanderson said it best in his 1965 book entitled Ivan Sanderson’s Book of Great Jungles. Sanderson grew up with a natural inclination towards adventure and learning. He hailed from Scotland but spent much [...] Read more →
Felix Weihs de Weldon, age 96, died broke in the year 2003 after successive bankruptcies and accumulating $4 million dollars worth of debt. Most of the debt was related to the high cost of love for a wife living with Alzheimer’s. Health care costs to maintain his first wife, Margot, ran $500 per [...] Read more →
? This video by AT Restoration is the best hands on video I have run across on the basics of classic upholstery. Watch a master at work. Simply amazing. Tools: Round needles: https://amzn.to/2S9IhrP Double pointed hand needle: https://amzn.to/3bDmWPp Hand tools: https://amzn.to/2Rytirc Staple gun (for beginner): https://amzn.to/2JZs3x1 Compressor [...] Read more →
Carya Nuts This Handbook is Published by SLMA or the Southeastern Lumber Manufacturer’s Association Click here to read the handbook or click on the link below for a faster download. Hardwood Handbook Home Top of Pg. Read more →
John Atkinson Grimshaw – Glasgow Saturday Night Home Top of Pg. Read more →
Nov. 5. 1898 Forest and Stream Pg. 371-372 The Black Grouper or Jewfish. New Smyrna, Fla., Oct. 21.—Editor Forest and Stream: It is not generally known that the fish commonly called jewfish. warsaw and black grouper are frequently caught at the New Smyrna bridge [...] Read more →
Como dome facade – Pliny the Elder – Photo by Wolfgang Sauber Work in Progress… THE VARNISHES. Every substance may be considered as a varnish, which, when applied to the surface of a solid body, gives it a permanent lustre. Drying oil, thickened by exposure to the sun’s heat or [...] Read more →
Man looks at severed hand and foot….for refusing to climb a tree to cut rubber for King Leopold Click here to read The Crime of the Congo by Arthur Conan Doyle Victim of King Leopold of Belgium Click on the link below for faster download. The [...] Read more →
DECORATED or “sumptuous” furniture is not merely furniture that is expensive to buy, but that which has been elaborated with much thought, knowledge, and skill. Such furniture cannot be cheap, certainly, but the real cost of it is sometimes borne by the artist who produces rather than by the man who may [...] Read more →
Reprint from the Royal Collection Trust Website The meeting between Henry VIII and Francis I, known as the Field of the Cloth of Gold, took place between 7 to 24 June 1520 in a valley subsequently called the Val d’Or, near Guisnes to the south of Calais. The [...] Read more →
Baking is a very similar process to roasting: the two often do duty for one another. As in all other methods of cookery, the surrounding air may be several degrees hotter than boiling water, but the food is no appreciably hotter until it has lost water by evaporation, after which it may [...] Read more →
Note on Watercolour: F.A. Molony (fl. 1930-1938) was a Major in the Royal Engineers. The National Army Museum hold his work. His work was also shown at an exhibition of officers work at the R.B.A. Galleries (Army Officers’ Art Society) Description from Youtube: June 2015 will see [...] Read more →
Cannone nel castello di Haut-Koenigsbourg, photo by Gita Colmar Without any preliminary cleaning the bronze object to be treated is hung as cathode into the 2 per cent. caustic soda solution and a low amperage direct current is applied. The object is suspended with soft copper wires and is completely immersed into [...] Read more →
Officers and men of the 13th Light Dragoons, British Army, Crimea. Rostrum photograph of photographer’s original print, uncropped and without color correction. Survivors of the Charge. Half a league, half a league, Half a league onward, All in the valley of Death Rode the six hundred. “Forward, the Light Brigade! Charge for the [...] Read more →
An angler with a costly pole Surmounted with a silver reel, Carven in quaint poetic scroll- Jointed and tipped with finest steel— With yellow flies, Whose scarlet eyes And jasper wings are fair to see, Hies to the stream Whose bubbles beam Down murmuring eddies wild and free. And casts the line with sportsman’s [...] Read more →
Saint Francis of Assisi, founder of the mendicant Order of Friars Minor, as painted by El Greco. Catholic religious order Catholic religious orders are one of two types of religious institutes (‘Religious Institutes’, cf. canons 573–746), the major form of consecrated life in the Roman Catholic Church. They are organizations of laity [...] Read more →
The following are transcripts of two letters written by the Founding Father Thomas Jefferson on the subject of seed saving. “November 27, 1818. Monticello. Thomas Jefferson to Henry E. Watkins, transmitting succory seed and outlining the culture of succory.” [Transcript] Thomas Jefferson Correspondence Collection Collection 89 Read more →
July 2, 1898 Forest and Stream, Fresh-Water Angling. No. IX.—The Two Crappies. BY FRED MATHER. Fishing In Tree Tops. Here a short rod, say 8ft., is long enough, and the line should not be much longer than the rod. A reel is not [...] Read more →
Add 3 quarts clover blossoms* to 4 quarts of boiling water removed from heat at point of boil. Let stand for three days. At the end of the third day, drain the juice into another container leaving the blossoms. Add three quarts of fresh water and the peel of one lemon to the blossoms [...] Read more →
Home Top of Pg. Read more →
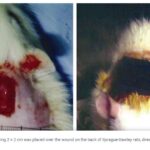
The Effect of Magnetic Fields on Wound Healing Experimental Study and Review of the Literature Steven L. Henry, MD, Matthew J. Concannon, MD, and Gloria J. Yee, MD Division of Plastic Surgery, University of Missouri Hospital & Clinics, Columbia, MO Published July 25, 2008 Objective: Magnets [...] Read more →
Life insurance certificate issued by the Yorkshire Fire & Life Insurance Company to Samuel Holt, Liverpool, England, 1851. On display at the British Museum in London. Donated by the ifs School of Finance. Photo by Osama Shukir Muhammed Amin FRCP(Glasg) From How to Make Money; and How to Keep it, Or, Capital and Labor [...] Read more →
And now for the transformation of Gray Gardens Home Top of Pg. Read more →
Home Top of Pg. Read more →
Aug. 13, 1898 Forest and Stream, Pg. 125 Game Bag and Gun. Indian Modes of Hunting. III.—Foxes. The fox as a rule is a most wily animal, and numerous are the stories of his cunning toward the Indian hunter with his steel traps. Read more →
Nov. 12, 1898 Forest and Stream Pg. 396 The Veterans to the Front. Ironton. O., Oct. 28.—Editor Forest and Stream: I mail you a target made here today by Messrs. E. Lawton, G. Rogers and R. S. Dupuy. Mr. Dupuy is seventy-four years old, Mr. Lawton seventy-two. Mr. Rogers [...] Read more →
Dominion, Royal St. Lawrence Yacht Club,Winner of Seawanhaka Cup, 1898. The Tail Wags the Dog. The following is a characteristic sample of those broad and liberal views on yachting which are the pride of the Boston Herald. Speaking of the coming races for the Seawanhaka international challenge cup, it says: [...] Read more →
The element copper effectively kills viruses and bacteria. Therefore it would reason and I will assert and not only assert but lay claim to the patents for copper mesh stints to be inserted in the arteries of patients presenting with severe cases of Covid-19 with a slow release dosage of [...] Read more →
H.F. Leonard was an instructor in wrestling at the New York Athletic Club. Katsukum Higashi was an instructor in Jujitsu. “I say with emphasis and without qualification that I have been unable to find anything in jujitsu which is not known to Western wrestling. So far as I can see, [...] Read more →
From Conquest of the Tropics by Frederick Upham Adams Chapter VI – Birth of the United Fruit Company Only those who have lived in the tropic and are familiar with the hazards which confront the cultivation and marketing of its fruits can readily understand [...] Read more →
Home Top of Pg. Read more →
Richard Barker KJ Title Pg. Robert Barker was the printer of the first edition of the King James Bible in 1611. He was the printer to King James I and son of Christopher Barker, printer to Queen Victoria I. Home Top of Pg. Read more →
Noel Desenfans and Sir Francis Bourgeois, circa 1805 by Paul Sandby, watercolour on paper The Dulwich Picture Gallery was England’s first purpose-built art gallery and considered by some to be England’s first national gallery. Founded by the bequest of Sir Peter Francis Bourgois, dandy, the gallery was built to display his vast [...] Read more →
Click here to view a copy of Arban’s Complete Conservatory Method for Cornet Click on the blue button to download a free copy of Arban’s Complete Conservatory Method for Cornet Arban's - 11.8MB For trumpet players wishing to practice daily using an iPad, simply click [...] Read more →
Cleaner for Gilt Frames. Calcium hypochlorite…………..7 oz. Sodium bicarbonate……………7 oz. Sodium chloride………………. 2 oz. Distilled water…………………12 oz. Home Top of Pg. Read more →
Home Top of Pg. Read more →
BLACKBERRY WINE 5 gallons of blackberries 5 pound bag of sugar Fill a pair of empty five gallon buckets half way with hot soapy water and a ¼ cup of vinegar. Wash thoroughly and rinse. Fill one bucket with two and one half gallons of blackberries and crush with [...] Read more →
Early Texas photo of Tarpon catch – Not necessarily the one mentioned below… July 2, 1898. Forest and Stream Pg.10 Texas Tarpon. Tarpon, Texas.—Mr. W. B. Leach, of Palestine, Texas, caught at Aransas Pass Islet, on June 14, the largest tarpon on record here taken with rod and reel. The [...] Read more →
This massive volume gives one a real visual sense of what it was like running a highly efficient colonial operation in the early 20rh Century. It will also go a long way to help anyone wishing to understand modern political intrigue in the Middle-East. Click here to read A Survey of Palestine [...] Read more →
The first published illustration of Nicotiana tabacum by Pena and De L’Obel, 1570–1571 (shrpium adversana nova: London). Tobacco can be used for medicinal purposes, however, the ongoing American war on smoking has all but obscured this important aspect of ancient plant. Tobacco is considered to be an indigenous plant of [...] Read more →
*note – Billesdon and Billesden have both been used to name the hunt. BILLESDEN COPLOW POEM [From “Reminiscences of the late Thomas Assheton Smith, Esq”] The run celebrated in the following verses took place on the 24th of February, 1800, when Mr. Meynell hunted Leicestershire, and has since been [...] Read more →
Click here to access the world’s most powerful Import/Export Research Database on the Planet. With this search engine one is able to access U.S. Customs and other government data showing suppliers for any type of company in the United States. Home Top of Pg. Read more →
Armorial tablet of the Stewarts – Falkland Palace Fife, Scotland. The Stewart Kings – King James I & VI to Charles II Six video playlist on the Kings of England: Home Top of Pg. Read more →
? Home Top of Pg. Read more →
Home Top of Pg. Read more →
NAPOLEON’S PHARMACISTS. Of the making of books about Napoleon there is no end, and the centenary of his death (May 5) is not likely to pass without adding to the number, but a volume on Napoleon”s pharmacists still awaits treatment by the student in this field of historical research. There [...] Read more →
THE ABC OF THE FEDERAL RESERVE SYSTEM WH Y THE FEDERAL RESERVE SYSTEM WAS CALLED INTO BEING, THE MAIN FEATURES OF ITS ORGANIZATION , AND HOW IT WORKS B Y EDWIN WALTER KEMMERER, PH.D. PROFESSOR OF ECONOMICS AND FINANCE IN PRINCETON UNIVERSITY AND MEMBER OF [...] Read more →
Over the years I have observed a decline in manners amongst young men as a general principle and though there is not one particular thing that may be asserted as the causal reason for this, one might speculate… Self-awareness and being aware of one’s surroundings in social [...] Read more →
From the classic British Movie, The Shooting Party, a 1985 British drama film directed by Alan Bridges based on Isabel Colegate’s 9th novel of the same name published in 1980 we find a scene set in the billiards parlor whereupon the host of the weekend shooting party Sir Randolph Nettleby walks in [...] Read more →
THE HATHA YOGA PRADIPIKA Translated into English by PANCHAM SINH Panini Office, Allahabad [1914] INTRODUCTION. There exists at present a good deal of misconception with regard to the practices of the Haṭha Yoga. People easily believe in the stories told by those who themselves [...] Read more →
Mocking Bird Food. Hemp seed……….2 pounds Rape seed………. .1 pound Crackers………….1 pound Rice…………….1/4 pound Corn meal………1/4 pound Lard oil…………1/4 pound Home Top of Pg. Read more →
As reported in the The Colac Herald on Friday July 17, 1903 Pg. 8 under Art Appreciation as a reprint from the Westminster Gazette ART APPRECIATION IN THE COMMONS. The appreciation of art as well as of history which is entertained by the average member of the [...] Read more →
The Hunt Saboteur is a national disgrace barking out loud, black mask on her face get those dogs off, get them off she did yell until a swift kick from me mare her voice it did quell and sent the Hunt Saboteur scurrying up vale to the full cry of hounds drowning out her [...] Read more →
Resolution adapted at the New Orleans Convention of the American Institute of Banking, October 9, 1919: “Ours is an educational association organized for the benefit of the banking fraternity of the country and within our membership may be found on an equal basis both employees and employers; [...] Read more →
Home Top of Pg. Read more →
Home Top of Pg. Read more →
Mortlake Tapestries at Chatsworth House Click here to learn more about the Mortlake Tapestries of Chatsworth The Mortlake Tapestries were founded by Sir Francis Crane. From the Dictionary of National Biography, 1885-1900, Volume 13 Crane, Francis by William Prideaux Courtney CRANE, Sir FRANCIS (d. [...] Read more →
Are you considering purchasing a copper water pitcher for storing drinking water but have questions about the effects on your health? The following study may help jump-start your research. Storing Drinking-water in Copper pots Kills Contaminating Diarrhoeagenic Bacteria ABSTRACT Microbially-unsafe water is [...] Read more →
Snipe shooting-Epistle on snipe shooting, from Ned Copper Cap, Esq., to George Trigger-George Trigger’s reply to Ned Copper Cap-Black partridge. —— “Si sine amore jocisque Nil est jucundum, vivas in &more jooisque.” -Horace. “If nothing appears to you delightful without love and sports, then live in sporta and [...] Read more →
Home Top of [...] Read more →
Gary Kravit is an airline pilot and artist. He also owns and operates https://theultimatetaboret.com. You may view Gary’s art at https://garrykravitart.blogspot.com/ Home Top of Pg. Read more →
VITRUVIUS The Ten Books on Architecture TRANSLATED By MORRIS HICKY MORGAN, PH.D., LL.D. LATE PROFESSOR OF CLASSICAL PHILOLOGY IN HARVARD UNIVERSITY WITH ILLUSTRATIONS AND ORIGINAL DESINGS PREPARED UNDER THE DIRECTION OF HERBERT LANGFORD WARREN, A.M. NELSON ROBINSON JR. PROFESSOR OF ARCHITECTURE IN HARVARD [...] Read more →
King Arthur, Legends, Myths & Maidens is a massive book of Arthurian legends. This limited edition paperback was just released on Barnes and Noble at a price of $139.00. Although is may seem a bit on the high side, it may prove to be well worth its price as there are only [...] Read more →
Home Top of Pg. Read more →
Home Top of Pg. Read more →
Click here to learn more about The Tallis Scholars Home Top of Pg. Read more →
Home Top of Pg. Read more →
Home Top of Pg. Read more →
ORIGIN OF THE APOTHECARY. The origin of the apothecary in England dates much further back than one would suppose from what your correspondent, “A Barrister-at-Law,” says about it. It is true he speaks only of apothecaries as a distinct branch of the medical profession, but long before Henry VIII’s time [...] Read more →
John Keats Four Seasons fill the measure of the year; There are four seasons in the mind of man: He has his lusty spring, when fancy clear Takes in all beauty with an easy span; He has his Summer, when luxuriously Spring’s honied cud of youthful thoughts he loves To ruminate, and by such [...] Read more →
Salmon and Sturgeon Caviar – Photo by Thor Salmon caviar was originated about 1910 by a fisherman in the Maritime Provinces of Siberia, and the preparation is a modification of the sturgeon caviar method (Cobb 1919). Salomon caviar has found a good market in the U.S.S.R. and other European countries where it [...] Read more →
Reprint from The Pitfalls of Speculation by Thomas Gibson 1906 Ed. THE PUBLIC ATTITUDE TOWARD SPECULATION THE public attitude toward speculation is generally hostile. Even those who venture frequently are prone to speak discouragingly of speculative possibilities, and to point warningly to the fact that an overwhelming majority [...] Read more →
The downloadable audio clip is of FDR’s Second Fireside Chat recorded on May 7th, 1933. FDR 2nd Fireside Chat - May 7, 1933 - 18.5MB The transcript that follows is my corrected version of the transcript that is found The American Presidency Project website that was created [...] Read more →
To Choose Poultry. When fresh, the eyes should be clear and not sunken, the feet limp and pliable, stiff dry feet being a sure indication that the bird has not been recently killed; the flesh should be firm and thick and if the bird is plucked there should be no [...] Read more →
Blackbeard’s Jolly Roger If you’re looking for that most refreshing of summertime beverages for sipping out on the back patio or perhaps as a last drink before walking the plank, let me recommend my Blunderbuss Mai Tai. I picked up the basics to this recipe over thirty years ago when holed up [...] Read more →
Welcome to Country House Essays. Enjoy. Home Top of Pg. Read more →
Absolutely Brilliant! And as I am quite certain you will become a fan, there’s more! Home Top of Pg. Read more →
Home Top of Pg. Read more →
Click here to visit Ovation Guitars Ovation Patent Drawing 1975 Click here to read a copy of the 1975 Patent for the Ovation Guitar Home Top of Pg. Read more →
Home Top of Pg. Read more →
How happy is he born and taught. That serveth not another’s will; Whose armour is his honest thought, And simple truth his utmost skill Whose passions not his masters are; Whose soul is still prepared for death, Untied unto the world by care Of public fame or private breath; Who envies none that chance [...] Read more →
Today I shall share a bit of market wisdom that will be hard to swallow for some Rolex owners, especially if they bought their Submariner at the top of the magical Covid Watch Bubble that has now collapsed. History often repeats itself, even in the stock market, but when [...] Read more →
Patek Phillipe hand makes the finest watches in the world. Click here to learn more. Home Top of Pg. Read more →
A Lecture Delivered at the Guildhall, March 2, 1853 by Rev. H.M. Scarth, M.A., Rector of Bathwick. To understand the ancient history of the country in which we live, to know something of the arts and manners of the people who have preceded us, to ascertain what we owe [...] Read more →
Mortlake Tapestries at Chatsworth House Click here to read copy of Daemonologie Home Top of Pg. Read more →
Jul. 23, 1898 Forest and Stream, Pg. 65 Horn Measurements. Editor Forest and Stream: “Record head.” How shamefully this term is being abused, especially in the past three years; or since the giant moose from Alaska made his appearance in public and placed all former records (so far as [...] Read more →
King George IV was known far and wide as the dandy king, incompetent, ugly, and vulgar. As Prince regent, prior to his assent to the throne, he kept fast company with Beau Brummel, King of Dandies, a man sixteen years his younger. And decadence followed. King George was a gambler, philanderer, and [...] Read more →
Home Top of Pg. Read more →
Home Top of Pg. Read more →
Home Top of Pg. Read more →
The greatest cause of failure in vinegar making is carelessness on the part of the operator. Intelligent separation should be made of the process into its various steps from the beginning to end. PRESSING THE JUICE The apples should be clean and ripe. If not clean, undesirable fermentations [...] Read more →
Guarea guidonia Recipe 5 Per Cent Alcohol 8-24 Grain – Heroin Hydrochloride 120 Minims – Tincture Euphorbia Pilulifera 120 Minims – Syrup Wild Lettuce 40 Minims – Tincture Cocillana 24 Minims – Syrup Squill Compound 8 Gram – Ca(s)ecarin (P, D, & Co.) 8-100 Grain Menthol Dose – One-half to one fluidrams (2 to [...] Read more →
A rhetorical question? Genuine concern? In this essay we are examining another form of matter otherwise known as national literary matters, the three most important of which being the Matter of Rome, Matter of France, and the Matter of England. Our focus shall be on the Matter of England or [...] Read more →
If a Woman asks you to Change, Politely Excuse Yourself and Walk out the Door; Forever Nobody changes; character is built early in life, and by the time one is involved in adult relationships, it is highly unlikely that one can rebuild one’s character. Recognizing this early on in ones adult [...] Read more →
TROF. C. F. HOLDFER AND HIS 183LBS. TUNA, WITH BOATMAN JIM GARDNER. July 2, 1898. Forest and Stream Pg. 11 The Tuna Record. Avalon. Santa Catalina Island. Southern California, June 16.—Editor Forest and Stream: Several years ago the writer in articles on the “Game Fishes of the Pacific Slope,” in [...] Read more →
BEEF JERKY Preparation. Slice 5 pounds lean beef (flank steak or similar cut) into strips 1/8 to 1/4 inch thick, 1 to 2 inches wide, and 4 to 12 inches long. Cut with grain of meat; remove the fat. Lay out in a single layer on a smooth clean surface (use [...] Read more →
The rigging of an old square rig in London, United Kingdom. Photograph taken by Melongrower. Home Top of Pg. Read more →
Sennen Cove at Dusk – photo by Jim Champion – 2005 Home Top of Pg. Read more →
Stoke Park Pavillions Stoke Park Pavilions, UK, view from A405 Road. photo by Wikipedia user Cj1340 From Wikipedia: Stoke Park – the original house Stoke park was the first English country house to display a Palladian plan: a central house with balancing pavilions linked by colonnades or [...] Read more →
Biograph Theater, where John Dillinger was gunned down by the FBI on July 22, 1934 The Great Depression was on—highway based crime was rampant, the gangsters dressed as well as the bankers they robbed, and and Henry Ford’s big beautiful V8 sedan was the getaway car of choice for both wheelman and [...] Read more →
Click here to access the Internet Archive of old Popular Mechanics Magazines – 1902-2016 Click here to view old Popular Mechanics Magazine Covers Home Top of Pg. Read more →
Home Top of Pg. Read more →
Home Top of Pg. Read more →
For years in the West African nation of Ghana medicine men have used a root and leaves from a plant called nibima(Cryptolepis sanguinolenta) to kill the Plasmodium parasite transmitted through a female mosquito’s bite that is the root cause of malaria. A thousand miles away in India, a similar(same) plant [...] Read more →
H. M. Scarth, Rector of Wrington By the death of Mr. Scarth on the 5th of April, at Tangier, where he had gone for his health’s sake, the familiar form of an old and much valued Member of the Institute has passed away. Harry Mengden Scarth was bron at Staindrop in Durham, [...] Read more →
Vishnu as the Cosmic Man (Vishvarupa) Opaque watercolour on paper – Jaipur, Rajasthan c. 1800-50 CLAIRVOYANCE AND OCCULT POWERS By Swami Panchadasi Copyright, 1916 By Advanced Thought Pub. Co. Chicago, Il INTRODUCTION. In preparing this series of lessons for students of [...] Read more →
Video courtesy of Imperial War Museums, UK Home Top of Pg. Read more →
Audubon started to develop a special technique for drawing birds in 1806 a Mill Grove, Pennsylvania. He perfected it during the long river trip from Cincinnati to New Orleans and in New Orleans, 1821. Home Top of [...] Read more →
Photo by Rebecca Humann Texas Tea Recipe 2 oz Cuervo Gold Tequila Home Top of [...] Read more →
Book Conservators, Mitchell Building, State Library of New South Wales, 29.10.1943, Pix Magazine The following is taken verbatim from a document that appeared several years ago in the Maine State Archives. It seems to have been removed from their website. I happened to have made a physical copy of it at the [...] Read more →
Click here to read the Swiss National Bank’s Chronicle of Monetary Events. Home Top of Pg. Read more →
Jan Verkolje Antonie van Leeuwenhoek was the first person to describe gout or uric acid crystals 1679. For one suffering gout, the following vitamins, herbs, and extracts may be worth looking into: Vitamin C Folic Acid – Folic Acid is a B vitamin and is also known as B9 – [Known food [...] Read more →
Artisans world-wide spend a fortune on commercial brand oil-based gold leaf sizing. The most popular brands include Luco, Dux, and L.A. Gold Leaf. Pricing for quart size containers range from $35 to $55 depending upon retailer pricing. Fast drying sizing sets up in 2-4 hours depending upon environmental conditions, humidity [...] Read more →
PAINTER-WORK, in the building trade. When work is painted one or both of two distinct ends is achieved, namely the preservation and the coloration of the material painted. The compounds used for painting—taking the word as meaning a thin protective or decorative coat—are very numerous, including oil-paint of many kinds, distemper, whitewash, [...] Read more →
Dutch artist Herman de Vries – Photo taken by son Vince The two videos below of Herman de Vries at work at the Venice Bienalle 2015 are quite inspiring. So inspiring in fact that I moved into a cave for two weeks and wrote Shakespearean tragedy with charcoal. Filled with great joy [...] Read more →
Oct. 22, 1898 Forest and Stream Pg. 324 An Alaskan Moose Head. Tacoma, Washington; Oct. 1.—Editor Forest and Stream: In your issue of March 6, 1897, you showed cut of a pair of moose horns belonging to me that spread 73 1/2 in.— at that time [...] Read more →
New York Stock Exchange Floor September 26,1963 The Specialist as a member of a stock exchange has two functions.’ He must execute orders which other members of an exchange may leave with him when the current market price is away from the price of the orders. By executing these orders on behalf [...] Read more →
by John Partridge,drawing,1825 From the work of Sir Charles Lock Eastlake entitled Materials for a history of oil painting, (London: Longman, Brown, Green, and Longmans, 1846), we learn the following: The effect of oil at certain temperatures, in penetrating “the minute pores of the amber” (as Hoffman elsewhere writes), is still more [...] Read more →
Home Top of Pg. Read more →
Home Top of Pg. Read more →
Kenilworth Abbey Fields – Photo by David Hunt Click here to read Kenilworth by Sir Walter Scott Click here to view Kenilworth Notes Home Top of Pg. Read more →
Testing the Irish Blue Terrier Breed in 1923. Home Top of Pg. Read more →
1 garlic clove, cut in half 1 8-oz. pkg. Philadelphia Brand Cream Cheese 3 tablespoons clam broth 1 7-to 7 1/2-oz. can minced clams, drained Home Top of [...] Read more →
A General Process for Making Wine. Gathering the Fruit Picking the Fruit Bruising the Fruit Vatting the Fruit Vinous Fermentation Drawing the Must Pressing the Must Casking the Must Spirituous Fermentation Racking the Wine Bottling and Corking the Wine Drinking the Wine GATHERING THE FRUIT. It is of considerable consequence [...] Read more →
The Queen Elizabeth Trust, or QEST, is an organisation dedicated to the promotion of British craftsmanship through the funding of scholarships and educational endeavours to include apprenticeships, trade schools, and traditional university classwork. The work of QEST is instrumental in keeping alive age old arts and crafts such as masonry, glassblowing, shoemaking, [...] Read more →
J.P. Morgan Patent #8,452,703 Method and system for processing internet payments using the electronic funds transfer network. Abstract Embodiments of the invention include a method and system for conducting financial transactions over a payment network. The method may include associating a payment address of an account [...] Read more →
Aw, the good old days, meet in the coffee shop with a few friends, click open the Zippo, inhale a glorious nosegay of lighter fluid, fresh roasted coffee and a Marlboro cigarette…. A Meta-analysis of Coffee Drinking, Cigarette Smoking, and the Risk of Parkinson’s Disease We conducted a [...] Read more →
Dec. 10, 1898 Forest and Stream Pg. 477-479 Zulu. The little ship shown in the accompanying plans needs no description, as she speaks for herself, a handsome and shipshape craft that a man may own for years without any fear that she will go to pieces [...] Read more →
ON THE ORIGIN OF SPECIES BY MEANS OF NATURAL SELECTION, OR THE PRESERVATION OF FAVOURED RACES IN THE STRUGGLE FOR LIFE. BY CHARLES DARWIN, M.A., FELLOW OF THE ROYAL, GEOLOGICAL, LINNÆAN, ETC., SOCIETIES ; AUTHOR OF ‘JOURNAL OF RESEARCHES DURING H.M.S. BEAGLE’S [...] Read more →
THE FOWLING PIECE, from the Shooter’s Guide by B. Thomas – 1811. I AM perfectly aware that a large volume might be written on this subject; but, as my intention is to give only such information and instruction as is necessary for the sportsman, I shall forbear introducing any extraneous [...] Read more →
THE FIRST step in producing a satisfactory crop of tobacco is to use good seed that is true to type. The grower often can save his own seed to advantage, if he wants to. Before topping is done, he should go over the tobacco field carefully to pick [...] Read more →
Home Top of Pg. Read more →
Home Top of Pg. Read more →
Click here to read the full text of the Hunting Act – 2004 Home Top of Pg. Read more →
Reprint from The Royal Collection Trust website: Kneller was born in Lubeck, studied with Rembrandt in Amsterdam and by 1676 was working in England as a fashionable portrait painter. He painted seven British monarchs (Charles II, James II, William III, Mary II, Anne, George I and George II), though his [...] Read more →
Muscadine Jelly 6 cups muscadine grape juice 6 cups sugar 1 box Kraft Sure Gel or Ball Fruit Jell Home Top of [...] Read more →
Click here to read The First Greek Book by John Williams White The First Greek Book - 15.7MB IN MEMORIAM JOHN WILLIAMS WHITE The death, on May 9, of John Williams White, professor of Greek in Harvard University, touches a large number of classical [...] Read more →
Home Top of Pg. Read more →
Fred Kummerow on statin drugs (excerpt) from Jeremy Stuart on Vimeo. Dr. Kummerow passed away at the ripe old age of 102 in 2017. Click here to visit Dr. Mercola’s website. Home Top of Pg. Read more →
The existence of large bodies of men having no other means of subsistence than those afforded by plunder, is, in all countries, too common to excite surprise; and, unhappily, organized bands of assassins are not peculiar to India! The associations of murderers known by the name of Thugs present, however, [...] Read more →
Home Top of Pg. Read more →
AB Bookman’s 1948 Guide to Describing Conditions: As New is self-explanatory. It means that the book is in the state that it should have been in when it left the publisher. This is the equivalent of Mint condition in numismatics. Fine (F or FN) is As New but allowing for the normal effects of [...] Read more →
“The Leda, in the Colonna palace, by Correggio, is dead-coloured white and black, with ultramarine in the shadow ; and over that is scumbled, thinly and smooth, a warmer tint,—I believe caput mortuum. The lights are mellow ; the shadows blueish, but mellow. The picture is painted on panel, in [...] Read more →
Bess of Harwick Four times the nuptial bed she warm’d, And every time so well perform’d, That when death spoil’d each husband’s billing, He left the widow every shilling. Fond was the dame, but not dejected; Five stately mansions she erected With more than royal pomp, to vary The prison of her captive When [...] Read more →
Home Top of Pg. Read more →
|